Jan 12, 2022
User-Centered Design - Putting Users First
Jan 12, 2022
User-Centered Design - Putting Users First
Jan 12, 2022
User-Centered Design - Putting Users First
Introduction
User-centered design (UCD) is a philosophy and process that places users at the center of the design and development of digital products. By prioritizing user needs, behaviors, and preferences, UCD ensures that products are intuitive, functional, and enjoyable to use. This blog explores the principles of user-centered design, its benefits, practical approaches for implementation, and examples of successful applications.
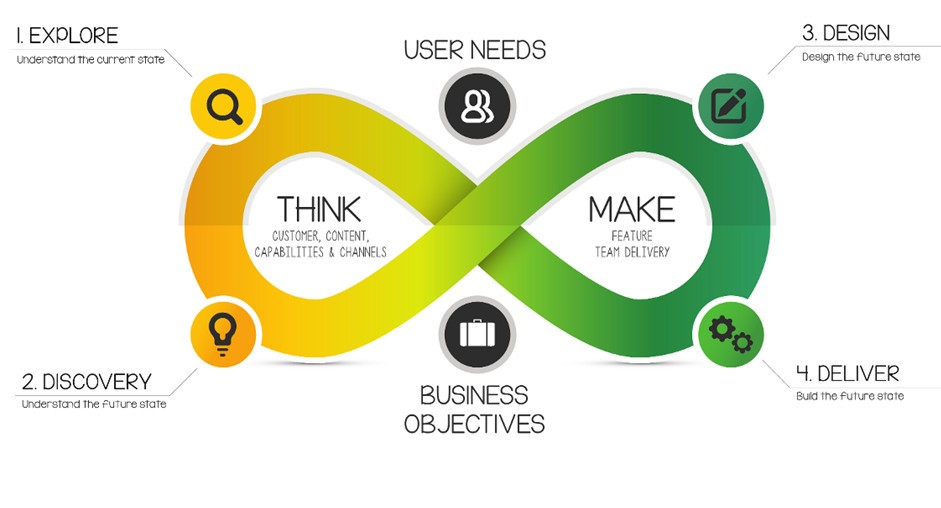
Principles of User-Centered Design
1. User Research
Understanding User Needs: Conducting research to uncover user goals, motivations, and pain points.
Empathy: Developing empathy for users to design solutions that meet their specific needs and expectations.
2. Iterative Design Process
Prototyping: Creating prototypes early in the design process to gather feedback and refine solutions.
Testing and Iteration: Iteratively testing designs with users to identify and address usability issues and improve the overall user experience.
3. Usability and Accessibility
Usability Testing: Evaluating the usability of designs to ensure they are intuitive and easy to navigate.
Accessibility: Designing products that are accessible to users with disabilities, ensuring inclusivity.
Benefits of User-Centered Design
1. Improved User Satisfaction
User-Friendly Interfaces: Designs that are intuitive and aligned with user expectations lead to higher user satisfaction.
Reduced Learning Curve: Products designed with UCD principles are easier for users to learn and use effectively.
2. Enhanced Product Success
Market Relevance: By addressing user needs and preferences, UCD increases the likelihood of product adoption and success in the market.
Iterative Improvement: Continuously refining designs based on user feedback leads to better products and competitive advantages.
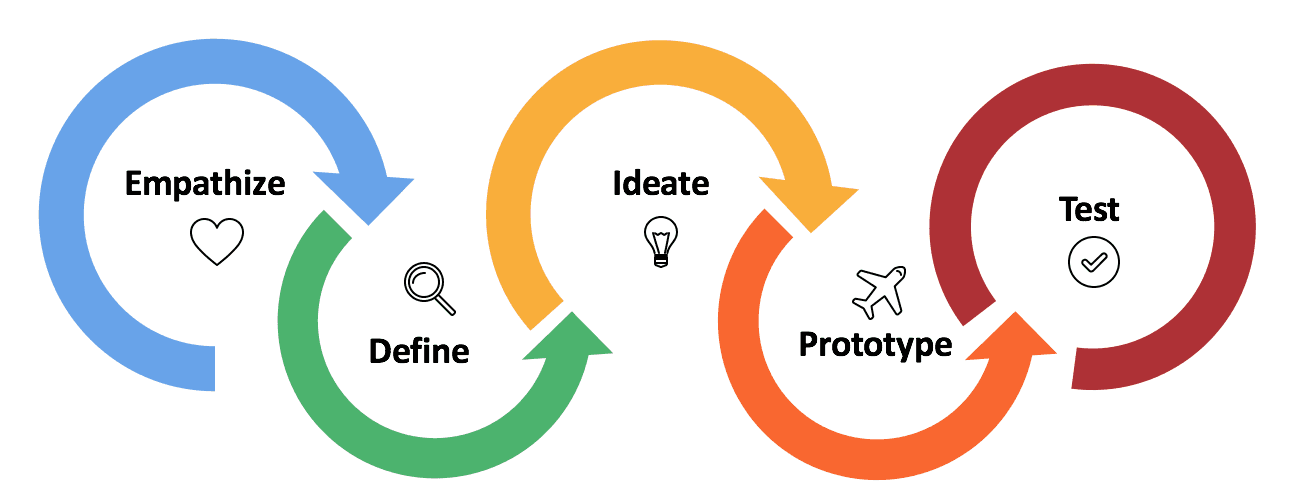
Practical Approaches for Implementing User-Centered Design
1. User Persona Development
Creating Personas: Developing detailed user personas based on research to represent different user segments and their behaviors.
2. Design Thinking Workshops
Collaborative Ideation: Engaging cross-functional teams in brainstorming sessions to generate innovative ideas and solutions.
Prototyping and Feedback: Rapidly prototyping ideas and gathering feedback from users to inform iterative design improvements.
3. Usability Testing and Feedback Loops
Moderated Testing: Conducting usability tests with real users to observe their interactions and gather qualitative feedback.
Iterative Refinement: Using feedback to iterate on designs and address usability issues before finalizing product features.
Examples of Successful User-Centered Design
1. Apple
Apple's design philosophy revolves around simplicity, intuitiveness, and user-centricity. Products like the iPhone and iPad are celebrated for their user-friendly interfaces and seamless user experiences.
2. Airbnb
Airbnb employs UCD principles to create a platform that meets the diverse needs of both hosts and guests. The design focuses on clarity, trust-building features, and personalized user experiences.
Case Study: Implementing User-Centered Design at Serene Solutions
Background
Company: Serene Solutions
Project: Development of a Meditation and Mindfulness App
Team:
Lead Designer: Emily Clark
Frontend Developer: David Nguyen
Product Manager: Sarah Johnson
Challenges
Serene Solutions aimed to develop a meditation and mindfulness app that resonated with users seeking stress relief and emotional wellness. Key challenges included understanding user motivations and designing a user-friendly interface that promoted engagement.
Approach
1. User Research and Persona Development
Emily Clark conducted user interviews and surveys to understand user motivations for using meditation apps and identified pain points in existing solutions. Personas were created to represent different user segments based on their goals and preferences.
2. Design and Prototyping
Emily collaborated with David Nguyen to create wireframes and prototypes that focused on simplicity, calming aesthetics, and intuitive navigation. They used Adobe XD for rapid prototyping and incorporated soothing color schemes and imagery.
3. Testing and Iteration
Sarah Johnson facilitated usability testing sessions with potential users to gather feedback on prototype designs. Feedback was used to iterate on features, refine the user interface, and enhance overall usability.
Results
Positive User Feedback: Early adopters praised the app for its calming design, ease of use, and effectiveness in promoting mindfulness and stress relief.
Increased Engagement: Analytics showed high user engagement metrics, including frequent app sessions and positive user reviews.
Market Success: The app gained traction in the mindfulness market, attracting a growing user base and receiving recognition for its user-centric design.
Conclusion
User-centered design is not just a methodology but a mindset that prioritizes understanding and addressing user needs throughout the design and development process. By embracing UCD principles, designers and teams can create products that are not only functional and intuitive but also deeply resonate with users, fostering loyalty and satisfaction. As digital experiences continue to evolve, the emphasis on putting users first will remain crucial for creating impactful and successful products that meet the diverse needs and expectations of today's users.
Introduction
User-centered design (UCD) is a philosophy and process that places users at the center of the design and development of digital products. By prioritizing user needs, behaviors, and preferences, UCD ensures that products are intuitive, functional, and enjoyable to use. This blog explores the principles of user-centered design, its benefits, practical approaches for implementation, and examples of successful applications.

Principles of User-Centered Design
1. User Research
Understanding User Needs: Conducting research to uncover user goals, motivations, and pain points.
Empathy: Developing empathy for users to design solutions that meet their specific needs and expectations.
2. Iterative Design Process
Prototyping: Creating prototypes early in the design process to gather feedback and refine solutions.
Testing and Iteration: Iteratively testing designs with users to identify and address usability issues and improve the overall user experience.
3. Usability and Accessibility
Usability Testing: Evaluating the usability of designs to ensure they are intuitive and easy to navigate.
Accessibility: Designing products that are accessible to users with disabilities, ensuring inclusivity.
Benefits of User-Centered Design
1. Improved User Satisfaction
User-Friendly Interfaces: Designs that are intuitive and aligned with user expectations lead to higher user satisfaction.
Reduced Learning Curve: Products designed with UCD principles are easier for users to learn and use effectively.
2. Enhanced Product Success
Market Relevance: By addressing user needs and preferences, UCD increases the likelihood of product adoption and success in the market.
Iterative Improvement: Continuously refining designs based on user feedback leads to better products and competitive advantages.

Practical Approaches for Implementing User-Centered Design
1. User Persona Development
Creating Personas: Developing detailed user personas based on research to represent different user segments and their behaviors.
2. Design Thinking Workshops
Collaborative Ideation: Engaging cross-functional teams in brainstorming sessions to generate innovative ideas and solutions.
Prototyping and Feedback: Rapidly prototyping ideas and gathering feedback from users to inform iterative design improvements.
3. Usability Testing and Feedback Loops
Moderated Testing: Conducting usability tests with real users to observe their interactions and gather qualitative feedback.
Iterative Refinement: Using feedback to iterate on designs and address usability issues before finalizing product features.
Examples of Successful User-Centered Design
1. Apple
Apple's design philosophy revolves around simplicity, intuitiveness, and user-centricity. Products like the iPhone and iPad are celebrated for their user-friendly interfaces and seamless user experiences.
2. Airbnb
Airbnb employs UCD principles to create a platform that meets the diverse needs of both hosts and guests. The design focuses on clarity, trust-building features, and personalized user experiences.
Case Study: Implementing User-Centered Design at Serene Solutions
Background
Company: Serene Solutions
Project: Development of a Meditation and Mindfulness App
Team:
Lead Designer: Emily Clark
Frontend Developer: David Nguyen
Product Manager: Sarah Johnson
Challenges
Serene Solutions aimed to develop a meditation and mindfulness app that resonated with users seeking stress relief and emotional wellness. Key challenges included understanding user motivations and designing a user-friendly interface that promoted engagement.
Approach
1. User Research and Persona Development
Emily Clark conducted user interviews and surveys to understand user motivations for using meditation apps and identified pain points in existing solutions. Personas were created to represent different user segments based on their goals and preferences.
2. Design and Prototyping
Emily collaborated with David Nguyen to create wireframes and prototypes that focused on simplicity, calming aesthetics, and intuitive navigation. They used Adobe XD for rapid prototyping and incorporated soothing color schemes and imagery.
3. Testing and Iteration
Sarah Johnson facilitated usability testing sessions with potential users to gather feedback on prototype designs. Feedback was used to iterate on features, refine the user interface, and enhance overall usability.
Results
Positive User Feedback: Early adopters praised the app for its calming design, ease of use, and effectiveness in promoting mindfulness and stress relief.
Increased Engagement: Analytics showed high user engagement metrics, including frequent app sessions and positive user reviews.
Market Success: The app gained traction in the mindfulness market, attracting a growing user base and receiving recognition for its user-centric design.
Conclusion
User-centered design is not just a methodology but a mindset that prioritizes understanding and addressing user needs throughout the design and development process. By embracing UCD principles, designers and teams can create products that are not only functional and intuitive but also deeply resonate with users, fostering loyalty and satisfaction. As digital experiences continue to evolve, the emphasis on putting users first will remain crucial for creating impactful and successful products that meet the diverse needs and expectations of today's users.
Introduction
User-centered design (UCD) is a philosophy and process that places users at the center of the design and development of digital products. By prioritizing user needs, behaviors, and preferences, UCD ensures that products are intuitive, functional, and enjoyable to use. This blog explores the principles of user-centered design, its benefits, practical approaches for implementation, and examples of successful applications.

Principles of User-Centered Design
1. User Research
Understanding User Needs: Conducting research to uncover user goals, motivations, and pain points.
Empathy: Developing empathy for users to design solutions that meet their specific needs and expectations.
2. Iterative Design Process
Prototyping: Creating prototypes early in the design process to gather feedback and refine solutions.
Testing and Iteration: Iteratively testing designs with users to identify and address usability issues and improve the overall user experience.
3. Usability and Accessibility
Usability Testing: Evaluating the usability of designs to ensure they are intuitive and easy to navigate.
Accessibility: Designing products that are accessible to users with disabilities, ensuring inclusivity.
Benefits of User-Centered Design
1. Improved User Satisfaction
User-Friendly Interfaces: Designs that are intuitive and aligned with user expectations lead to higher user satisfaction.
Reduced Learning Curve: Products designed with UCD principles are easier for users to learn and use effectively.
2. Enhanced Product Success
Market Relevance: By addressing user needs and preferences, UCD increases the likelihood of product adoption and success in the market.
Iterative Improvement: Continuously refining designs based on user feedback leads to better products and competitive advantages.

Practical Approaches for Implementing User-Centered Design
1. User Persona Development
Creating Personas: Developing detailed user personas based on research to represent different user segments and their behaviors.
2. Design Thinking Workshops
Collaborative Ideation: Engaging cross-functional teams in brainstorming sessions to generate innovative ideas and solutions.
Prototyping and Feedback: Rapidly prototyping ideas and gathering feedback from users to inform iterative design improvements.
3. Usability Testing and Feedback Loops
Moderated Testing: Conducting usability tests with real users to observe their interactions and gather qualitative feedback.
Iterative Refinement: Using feedback to iterate on designs and address usability issues before finalizing product features.
Examples of Successful User-Centered Design
1. Apple
Apple's design philosophy revolves around simplicity, intuitiveness, and user-centricity. Products like the iPhone and iPad are celebrated for their user-friendly interfaces and seamless user experiences.
2. Airbnb
Airbnb employs UCD principles to create a platform that meets the diverse needs of both hosts and guests. The design focuses on clarity, trust-building features, and personalized user experiences.
Case Study: Implementing User-Centered Design at Serene Solutions
Background
Company: Serene Solutions
Project: Development of a Meditation and Mindfulness App
Team:
Lead Designer: Emily Clark
Frontend Developer: David Nguyen
Product Manager: Sarah Johnson
Challenges
Serene Solutions aimed to develop a meditation and mindfulness app that resonated with users seeking stress relief and emotional wellness. Key challenges included understanding user motivations and designing a user-friendly interface that promoted engagement.
Approach
1. User Research and Persona Development
Emily Clark conducted user interviews and surveys to understand user motivations for using meditation apps and identified pain points in existing solutions. Personas were created to represent different user segments based on their goals and preferences.
2. Design and Prototyping
Emily collaborated with David Nguyen to create wireframes and prototypes that focused on simplicity, calming aesthetics, and intuitive navigation. They used Adobe XD for rapid prototyping and incorporated soothing color schemes and imagery.
3. Testing and Iteration
Sarah Johnson facilitated usability testing sessions with potential users to gather feedback on prototype designs. Feedback was used to iterate on features, refine the user interface, and enhance overall usability.
Results
Positive User Feedback: Early adopters praised the app for its calming design, ease of use, and effectiveness in promoting mindfulness and stress relief.
Increased Engagement: Analytics showed high user engagement metrics, including frequent app sessions and positive user reviews.
Market Success: The app gained traction in the mindfulness market, attracting a growing user base and receiving recognition for its user-centric design.
Conclusion
User-centered design is not just a methodology but a mindset that prioritizes understanding and addressing user needs throughout the design and development process. By embracing UCD principles, designers and teams can create products that are not only functional and intuitive but also deeply resonate with users, fostering loyalty and satisfaction. As digital experiences continue to evolve, the emphasis on putting users first will remain crucial for creating impactful and successful products that meet the diverse needs and expectations of today's users.